June 28th 2022
The Pear Cut Diamond Guide
By Devin Jones
Pear Cut Diamonds
The pear cut or pear shaped diamond has a unique and eye catching shape, something of a hybrid between a round cut and a marquise cut. The diamond is rounded on one end and tapers to a triangular point, resembling a classic teardrop shape. Like all fancy cut diamonds (non-round cut diamonds), the pear cut diamond is cut more for its unique dimensions than to optimize for sparkle. That said, the pear cut design can still offer plenty of spectacular light performance.
Pear cut diamonds are the sixth most popular diamond shape and account for about 3% of all diamonds searched for on StoneAlgo. The most popular shapes are round (47%), oval (14%), cushion (7%), emerald, 4.5%), and radiant (4.1%).
While pear cut diamonds aren't the most popular shape, most diamond shoppers choose them for just that reason: they're a unique style that melds elements of the classic with the bold. Pear cut diamonds tend to cost about 33% less than an equivalent round cut diamond, which is on par with other fancy shapes we've studied. That's probably why pear shaped diamonds have been growing in popularity month over month for the past couple of years according to data from our diamond search engine.
Pros & Cons of Pear Cut Diamonds
There are many reasons to love pear shaped diamonds, but there are also a few concerns we have when picking out the perfect one. Here are our top pros & cons for pear shaped diamonds:
Pear Cut Pros
- Unique design that stands out in an engagement ring
- Increasing in popularity
- Less expensive than round cut diamonds
- Graceful and flattering shape
- Can be worn pointing towards the wrist or the fingers (can switch it up daily for those who bore easily)
Pear Cut Cons
- Pointed end is more vulnerable to damage than a round cut diamond would be (more on this later)
- Fewer diamonds available in this cut than most other shapes make it hard to find the perfect diamond
- Lower color grade diamonds can appear yellow more easily (avoid I color and below)
While selection can be limited for pear cut diamonds, our diamond search engine aggregates diamond inventory from 10+ top-rated jewelers, offering diamond shoppers the largest possible selection of pear shaped diamonds (or any shape for that matter.
Pear Cut Diamond History
According to gemsociety.org, the pear cut diamond originated in Belgium around the year 1475 with the diamond cutter Lodewyk van Bercken. Pear cut diamonds were developed around the same time that van Bercken invented his diamond-polishing wheel which allowed him to more precisely cut diamonds with symmetrical facts. This innovation meant that unique cuts like the pear shape became possible for the first time. The original design for a pear shape diamond included 58 facets (just like the round and oval cut diamond) and today's design is largely unchanged, featuring the same number of facets to help optimize light performance (fire, brilliance, and scintillation).
Ideal Proportions for Pear Cut Diamonds
Unlike round cut diamonds, pear cut diamonds do not have a standard set of parameters that quality as good, very good, or excellent cut. In fact, pear cut diamonds do not receive cut grades from either the GIA or AGS. If you read our oval cut diamond guide you may recall that the AGS does grade oval brilliant cut diamonds (as well as emerald and princess cuts) but the pear cut diamond is just too difficult to grade for light performance despite the fact that it shares a common 58 facets with its cousins the oval and round cut diamonds.
One of the advantages that StoneAlgo has is a massive data set of both diamond inventory which allows us to hone in on the most popular angles and proportions for pear cut diamonds. Below are the results on our research regarding the most common proportions for pear cut diamonds in our massive diamond inventory database over over 2 million available stones.
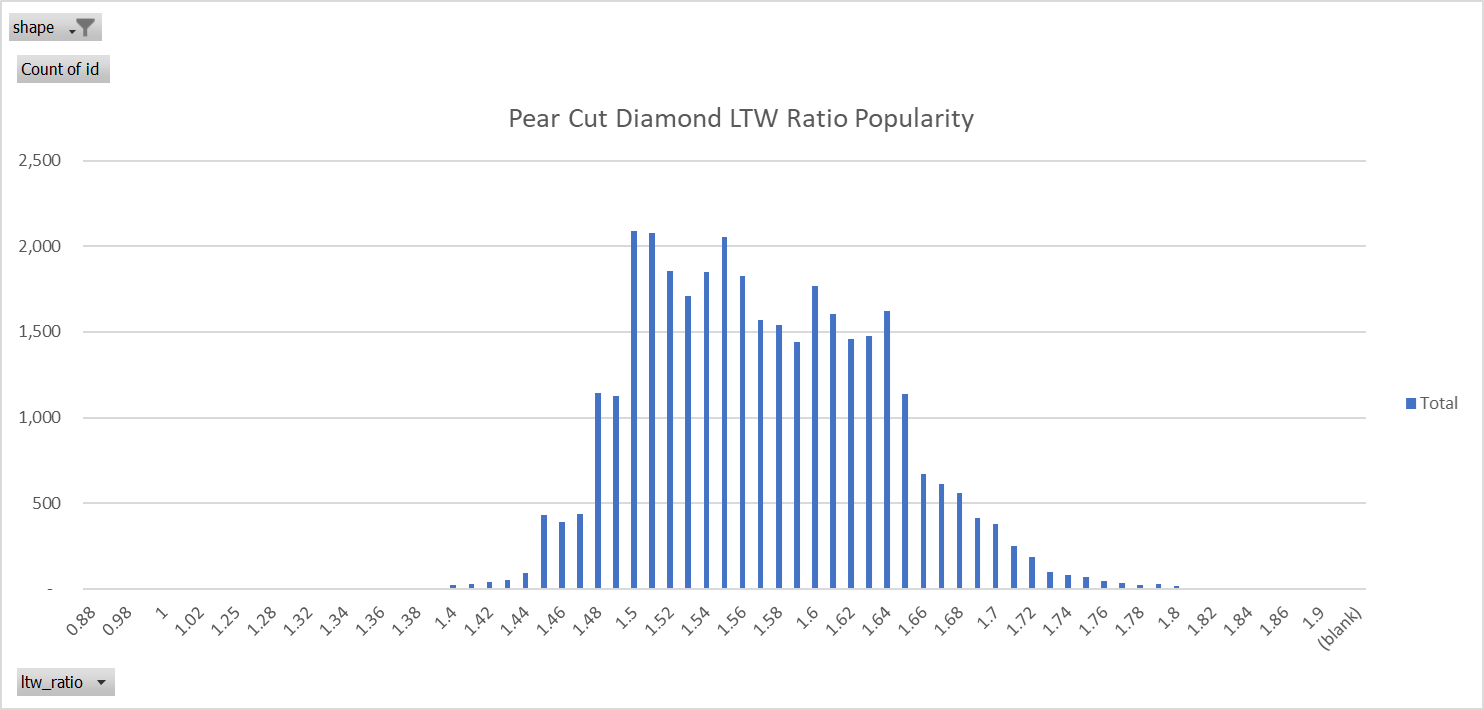
Pear Cut Length to Width Ratio
The most popular length to width ratio for pear cut diamonds is 1.50. The ideal proportions for a pear cut diamond appear to be a length to width ratio of 1.50 - 1.65 according to the data we collected.
Pear Cut Symmetry
While most of the dimensions of your pear cut diamond are purely subjective (choose what you love), symmetry is very objective. A simple way to think about symmetry is to ask yourself how similar the left half of the diamond looks to the right half. The GIA and AGS both grade pear cut diamond symmetry and we always recommend you purchase a stone with GIA Excellent or AGS Ideal symmetry grades.
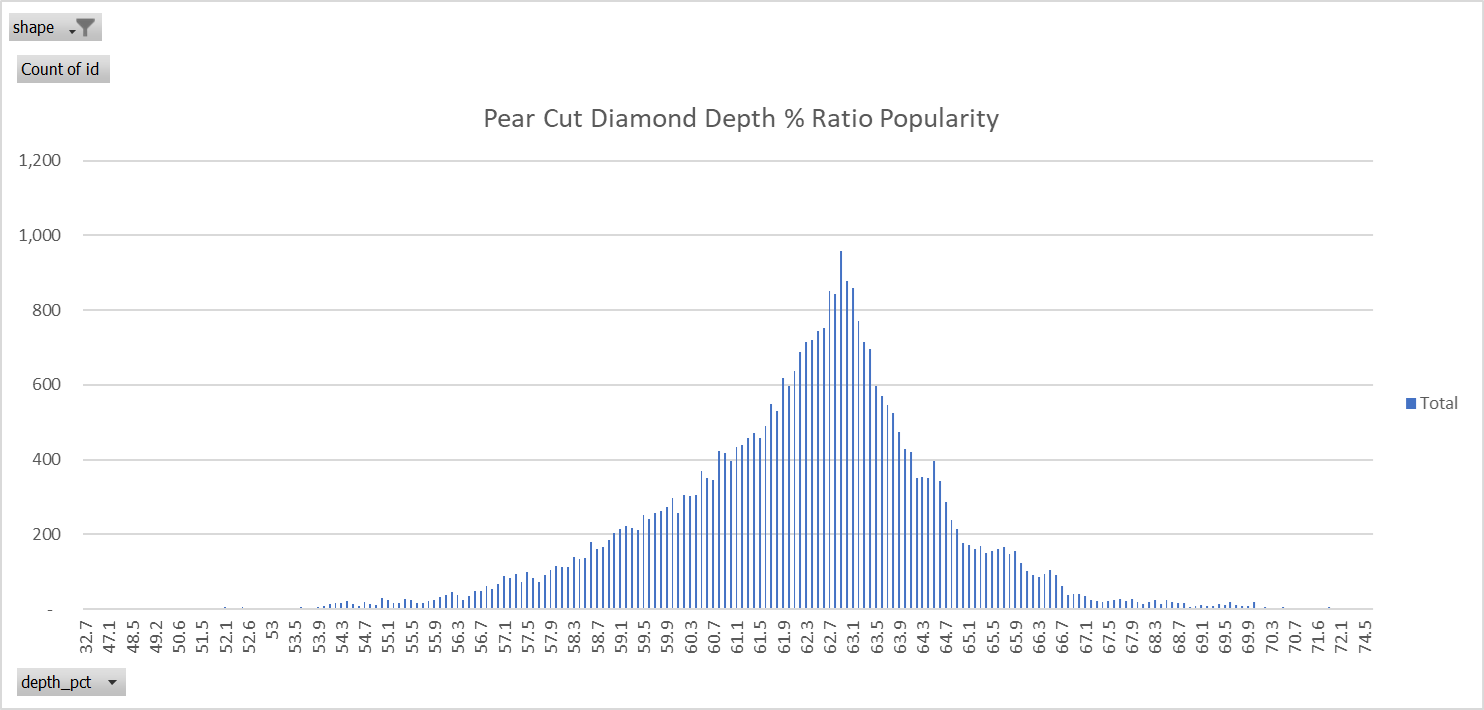
Pear Cut Depth Percentage
The most popular depth percentage for pear cut diamonds is 63.0%. The majority of pear cut diamond shoppers search for depth percentages between 61% and 64.5%, with a steep drop off after 64.5%. This drop off can be partially explained by the fact that deeper diamonds tend to face up smaller since much of the carat weight is allocated to the depth of the diamond, not the length or width. We call this property the diamond's "visual carat weight" and you see this calculation on any pear cut diamond in our diamond search engine.
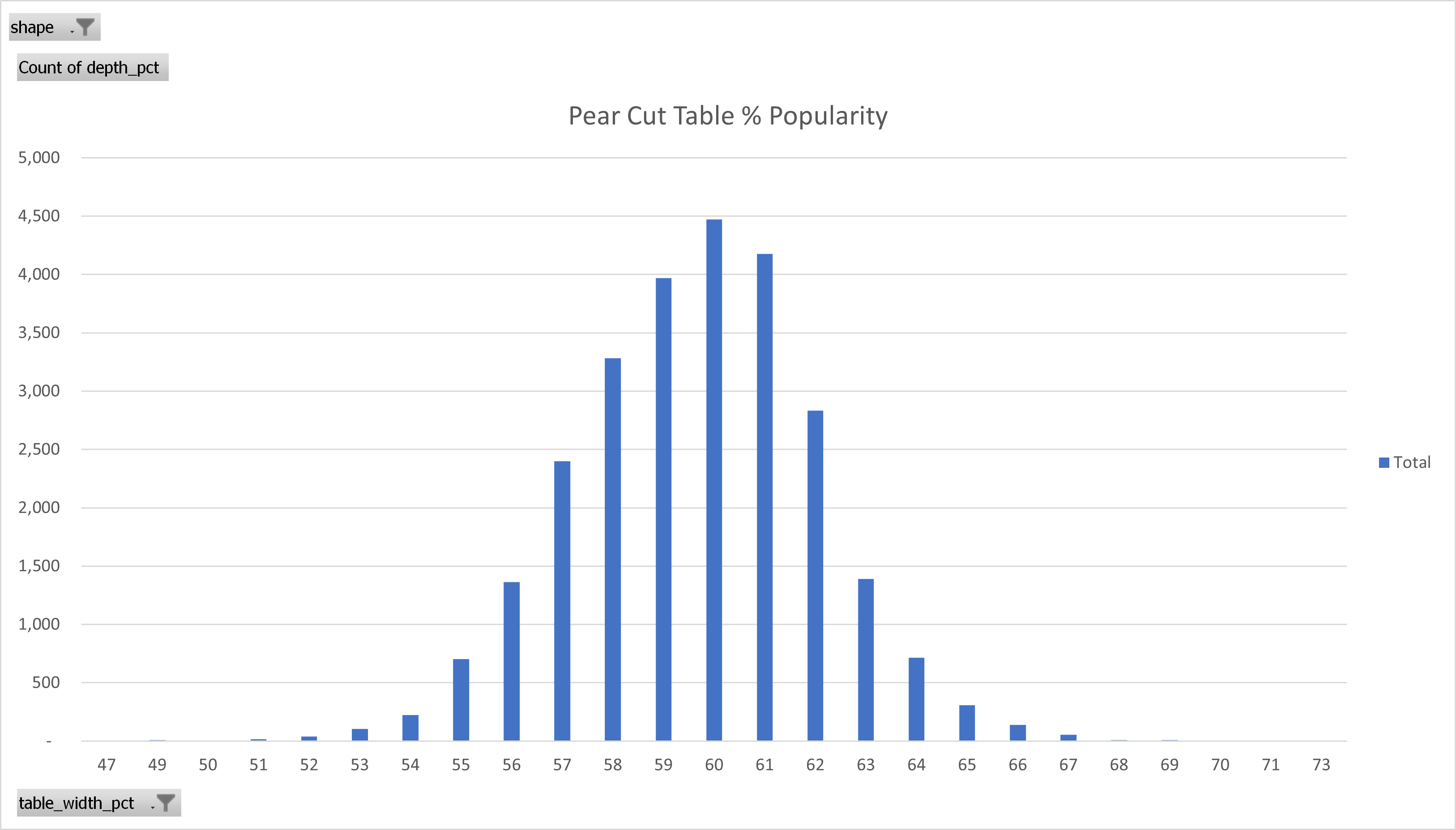
Pear Cut Table Percentage
The most popular pear cut diamond percentages follow a very predictable bell curve as you can see below. The most popular table percentage for pear cut diamonds is 60% and it appears most diamond shoppers search for pear cut table percentages between 57% - 62%.
Pear Cut Diamond Prices
Pear cut diamonds are much less expensive than round cut diamonds and tend to be priced similar to most other fancy shape diamonds. Diamond pricing boils down to two main factors: how expensive it is to cut the specific shape and the natural supply/demand imbalances that occur as certain shapes gain or lose popularity faster than expected.
The most expensive diamond shape is round cut because it yields the smallest finished diamond per carat of rough diamond, meaning there is low yield from the diamond cutting process (there's a lot of waste). Pear cut diamonds are less wasteful, and that savings is passed on to diamond shoppers in the form of lower prices. Pear cut diamonds are about 33% less expensive per carat than round cut diamonds.
| Carat Weight | Diamond Price | Price Per Carat |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | $1,338 | $2,676 |
| 1 | $5,575 | $5,575 |
| 2 | $25,195 | $12,598 |
| 3 | $48,970 | $16,323 |
The above data is from June 2022. To check today's live diamond prices please use our diamond prices tool.
- 0.5 carat pear cut diamond prices
- 1 carat pear cut diamond prices
- 2 carat pear cut diamond prices
- 3 carat pear cut diamond prices
Bow Tie Effect in Pear Cut Diamonds
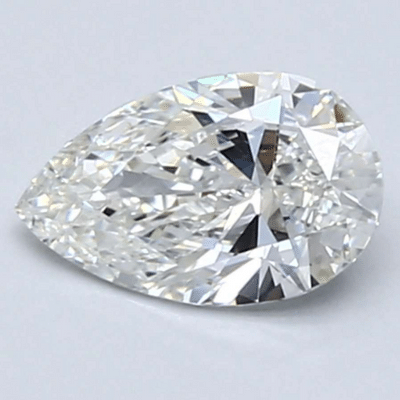
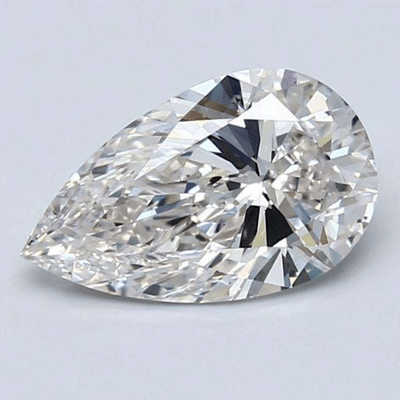
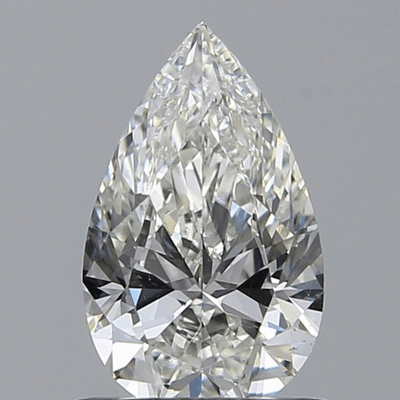
Pear cut diamonds, like oval cuts, sometimes show a dark bow tie shaped pattern on the table and crown of the diamond due to the way light reflects within the stone. This effect cannot easily be predicted based solely on raw data from the diamond's GIA or AGS certificate. This is why it's vitally important that you see your diamond in images or videos before you buy. Here are some examples of pear cut diamonds with pronounced bow tie effects. You can get a better understanding of how the bow tie looks from various angles by viewing videos of the diamonds, available on the jeweler's websites.
Click the above diamonds for more details
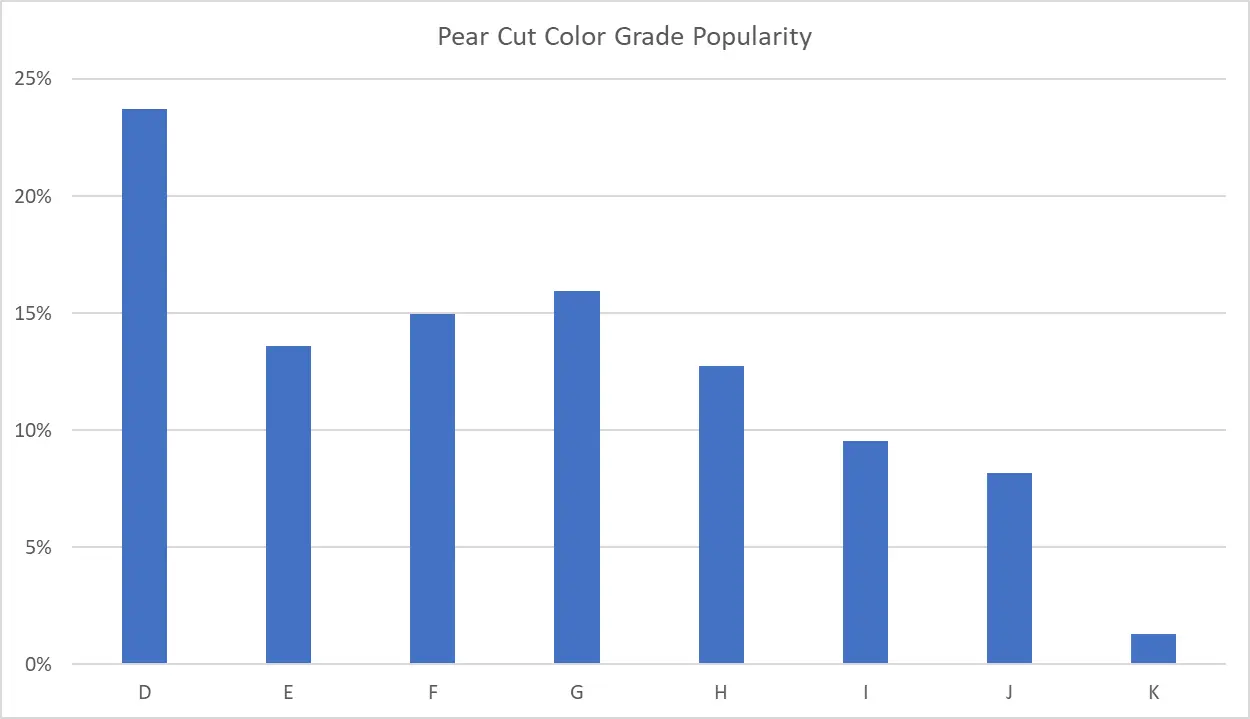
Best Color Grades for Pear Cut Diamonds
The most popular color grade for pear cut diamonds is D color and it's not even close. D color diamonds account for about 24% of pear cut diamonds selected by StoneAlgo users, while G color ranks at a distant second place at 16%. Taking a look at the data below, we can see that a peak forms around G color and the most significant drop off (other than D color) appears between J and K color. Taking all of this into account, we recommend G color for most diamond shoppers since it's a popular color grade for pear cut diamonds and offer far better value than D color diamonds.
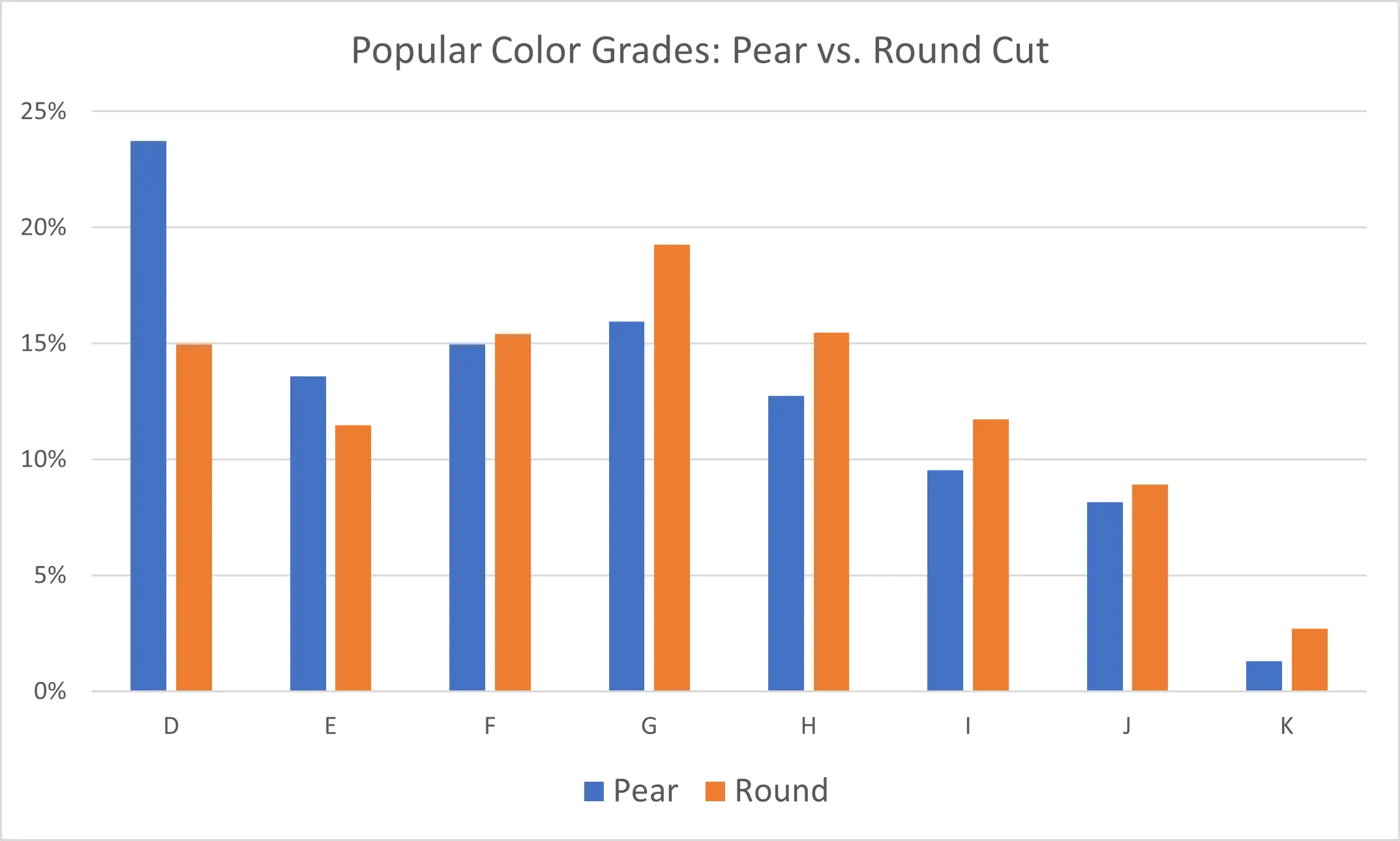
Pear vs Round Cut Diamond
To reiterate just how extreme the spike in D color is for pear shapes, here's a comparison of pear vs. round cut diamonds by most popular color grade. Pear cut diamonds tend to show their color more easily than round cut diamonds because a round cut diamond typically offers better sparkle that compensates for some of the natural color in the diamond. As you can see below, round cut diamonds have a similar pattern to pear cut diamonds in terms of color grade popularity but the D color grade is far less popular relative to G color for round cut diamonds.